Artwork Basics
Scale
Bleed
Trim Bleed
Finish Bleed
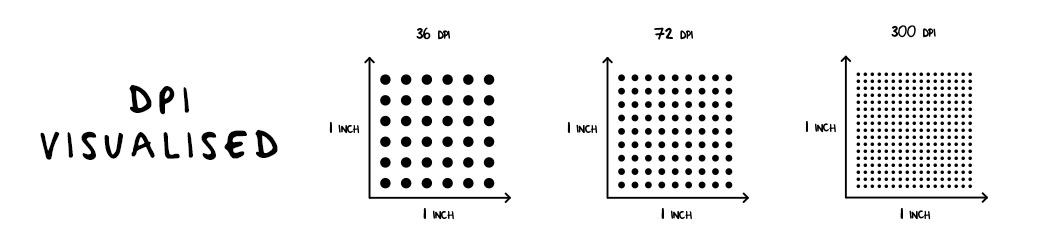
Dots Per Inch
Dots Per Inch is the measure of how many dots there are per inch of printed material. The higher the number of dots the higher the quality of print. It is used to express either the quality a print is printed at or an Image's Resolution.
A good way of visualising this is the diagram below.
Minimum Recommend Artwork Dpi
| Work Type | Minimum DPI |
| Business Cards & Leaflets | 300dpi |
| A0 Poster and Bigger | 100dpi |
Though we can print at lower resolutions depending on the viewing distance we always recommend a minimum DPI of 100
Dpi at Scale
| Scale | Multiply DPI / Scale By | Example |
| 25% | 4 | |
| 33% | 3 | |
| 10% | 10 | |
| 1% | 100 |
Viewing Distance vs DPI
| Viewing Distance | Min Resolution |
| 0.6m / 2ft | 300 dpi |
| 1m / 3.3ft | 180 dpi |
| 1.5m / 5ft | 120 dpi |
| 2m / 6.5ft | 90 dpi |
| 3m / 10ft | 60 dpi |
| 5m / 16ft | 35 dpi |
| 10m / 33ft | 18 dpi |
| 15m / 50ft | 12 dpi |
| 50m / 160ft | 4 dpi |
| 60m / 200ft | 3 dpi |
| 200m / 650ft | 1 dpi |
Low Resolution vs High Resolution
Low resolution is another way of saying low DPI or poor quality. High Resolution is another way of saying high DPI or high quality.
The images below show a high DPI (High Resolution) vs a low DPI (Low Resolution) image.
While you can convert a low resolution image to a high resolution image, You cannot convert a Low Resolution image to a High Resolution. There is an alternative called upscaling, which you can read about below.
Upscaling Images
Upscaling is the process of converting an image from Low Resolution to High Resolution. Basic upscaling is the simplest way of stretching a lower resolution image onto a larger display. Pixels from the lower resolution image are copied and repeated to fill out all the pixels of the higher resolution display.
More advance processes include Dithering (blurring the dots as you enlarge so you don't get a block effect) or AI (using computer prediction based on the surrounding dots to predict what the image should look like at a larger size).

No Comments